Integrating Kubernetes with Gitlab CI

In the final post of this series, we hook Kubernetes (k8s) to up Gitlab, and deploy our Go service to our k8s system. We will be using minikube as our Kubernetes provider.
All the code for this article can be found here
Hint: In Visual Studio Code add Microsoft Kubernetes extension or Cloud Code to see k8s details from the editor
Install kubernetes CLI
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl/
Check
kubectl version
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"14", GitVersion:"v1.14.3", GitCommit:"5e53fd6bc17c0dec8434817e69b04a25d8ae0ff0", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2019-06-06T01:44:30Z", GoVersion:"go1.12.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"darwin/amd64"}
Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"14", GitVersion:"v1.14.0", GitCommit:"641856db18352033a0d96dbc99153fa3b27298e5", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2019-03-25T15:45:25Z", GoVersion:"go1.12.1", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
Install Minikube
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-minikube/
Start
minikube startEnable docker login from within minikube
Add the key created in the first post to minikube:
Unfortunately we need to run this every time you start minikube.
cat ~/.docker/certs.d/gitlab.lightphos.com\:5555/ca.crt | minikube ssh "sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker/certs.d/gitlab.lightphos.com:5555 && sudo tee /etc/docker/certs.d/gitlab.lightphos.com:5555/ca.crt"
minikube ssh "sudo systemctl restart docker"
Check login:
minikube ssh
docker login gitlab.lightphos.com:5555
If successful good to go. Exit the shell.
Deploy Hi.go Service to MiniKube K8s manually
Set up docker access secret calling it gitlab.lightphos (using Gitlab username and password for DOCKER_USER and DOCKER_PASSWORD). Note: This will be within the default namespace.
kubectl create secret docker-registry gitlab.lightphos --docker-server=https://gitlab.lightphos.com:5555 --docker-username=DOCKER_USER --docker-password=DOCKER_PASSWORD
Create a file manifest/deployment.yml, with the following:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hi-deployment
labels:
app: hi
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hi
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hi
spec:
containers:
- name: hi
image: gitlab.lightphos.com:5555/sr/hi:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8090
imagePullSecrets:
- name: gitlab.lightphoskubectl apply -f manifest/deployment.yml
If the deployment doesn't go as planned for whatever reason, start again by first deleting it
kubectl delete deployment hi-deployment
Check it:
kubectl get deployments
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
hi-deployment 1/1 1 1 10sExpose a service so we can see it from the host:
kubectl expose deployment hi-deployment --type=NodePort --port=8090
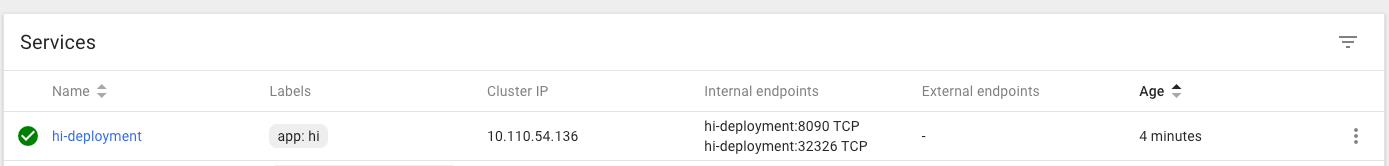
kubectl get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
hi-deployment NodePort 10.110.54.136 <none> 8090:32326/TCP 9s
minikube service hi-deployment
Should fire up in the browser.
http://192.168.99.101:32326/there
Dashboard should show the service/deployments/pods operational:
This will stay running even when the pod is deleted.
Try
kubectl get pods
kubectl delete pod <pod>
kubectl get pods
A new one should be stood up instantly.
Navigate back to the url.
Should still be running. This, the power of k8s.
delete deployment and service.
kubectl delete deployment hi-deployment
Gitlab Kubernetes Integration
Back to the local gitlib at http://gitlib.lightphos.com:30080
White list minikube ip, $(minikube ip):
Login as root
Admin area -> Settings -> Network -> Outbound Requests (check all boxes)
add the following (whatever the minikube ip is):
192.168.99.101
Login as yourself navigate to your project (hi):
Gitlab -> hi -> Operations -> Kubernetes -> Add existing cluster
For API url add 192.168.99.101:8443 (minikube)
Get Default CA Certificate:
kubectl get secret $(kubectl get secrets | grep default | cut -f 1 -d ' ') -o jsonpath="{['data']['ca\.crt']}" | base64 --decode
Use the resulting details for the CA certificate
for Service Token create a file manifest/gitlab-service-account.yml. Note: This gives wide ranging permissions, a more restrictive rbac.yml is shown below.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: gitlab-admin
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: gitlab-admin
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: gitlab-admin
namespace: kube-system
Apply it to k8s
kubectl apply -f manifest/gitlab-service-account.yml
Retrieve the token:
kubectl -n kube-system describe secret $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | grep gitlab-admin | awk '{print $1}')
Add it to the Service Token field.
Check the Gitlab-managed cluster option.
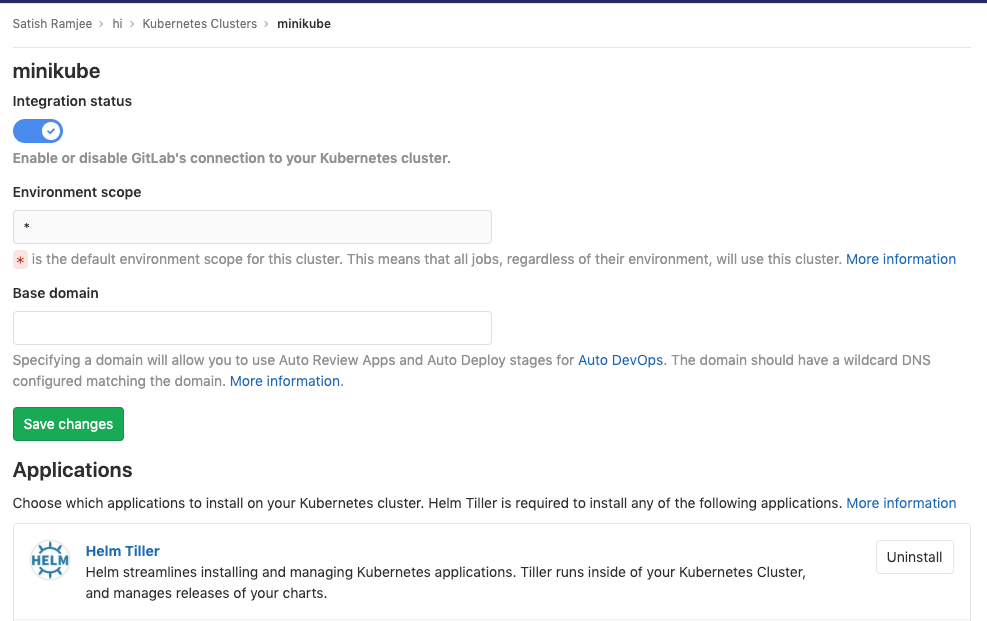
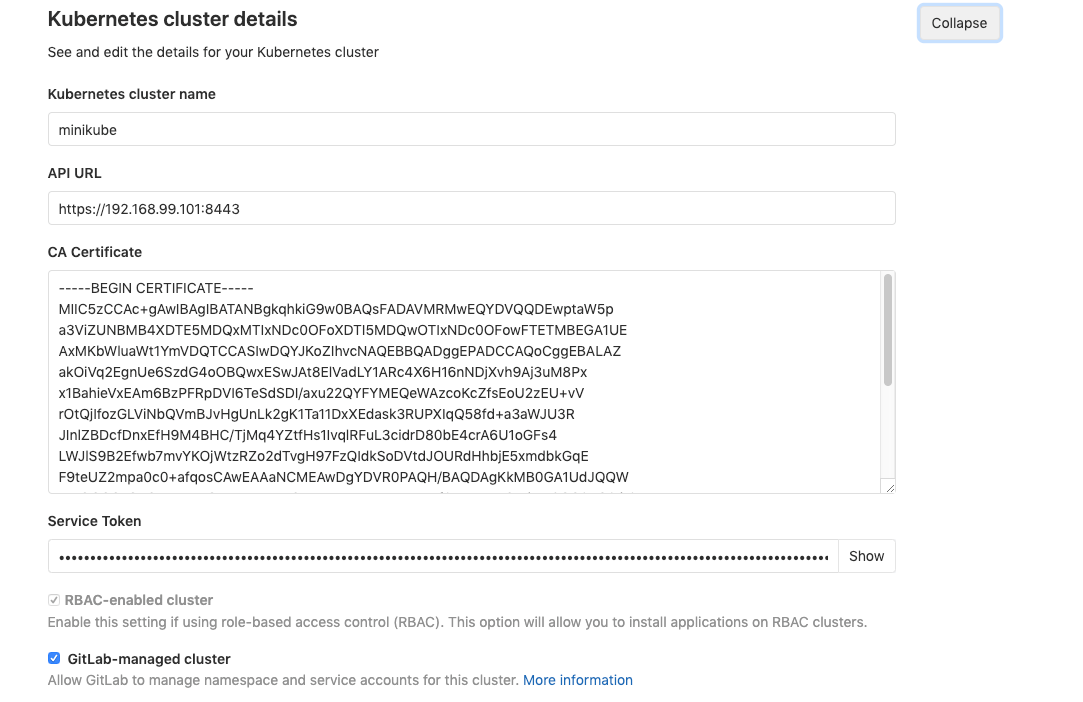
After adding the CA and Token, minikube k8s will be integrated with Gitlab. You can test the connection by installing Helm Tiller.
NOTE: The namespace in K8s defaults to <project_name>-<project_id>-<environment>. See below for how to set it to a fixed name.
Deploying Hi Go service to K8s via Gitlab CI Automation
Update the previous .gitlab-ci.yml file to this:
variables:
REPO_NAME: ${CI_REGISTRY}/${CI_PROJECT_PATH}
CONTAINER_IMAGE: ${CI_REGISTRY}/${CI_PROJECT_PATH}:${CI_BUILD_REF_NAME}_${CI_BUILD_REF}
CONTAINER_IMAGE_LATEST: ${CI_REGISTRY}/${CI_PROJECT_PATH}:latest
DOCKER_DRIVER: overlay2
before_script:
- mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/$(dirname $REPO_NAME)
- ln -svf $CI_PROJECT_DIR $GOPATH/src/$REPO_NAME
- cd $GOPATH/src/$REPO_NAME
stages:
- test
- build
- release
- deploy
format:
image: golang:latest
stage: test
script:
- go fmt $(go list ./... | grep -v /vendor/)
- go vet $(go list ./... | grep -v /vendor/)
- go test -race $(go list ./... | grep -v /vendor/)
compile:
image: golang:latest
stage: build
script:
- go build -race -ldflags "-extldflags '-static'" -o $CI_PROJECT_DIR/hi
artifacts:
paths:
- hi
release:
image: docker:19.03.1
stage: release
before_script:
- echo ${CONTAINER_IMAGE}
- echo $CI_BUILD_TOKEN | docker login -u gitlab-ci-token --password-stdin ${CI_REGISTRY}
script:
- docker build -t ${CONTAINER_IMAGE} -t ${CONTAINER_IMAGE_LATEST} .
- docker push ${CONTAINER_IMAGE}
- docker push ${CONTAINER_IMAGE_LATEST}
deploy:
image: dtzar/helm-kubectl
stage: deploy
environment:
name: production # you need to specify an environment to access KUBE vars
url: http://hi.info/earth
script:
- echo CI_PROJECT_ID=$CI_PROJECT_ID
- echo KUBE_URL=$KUBE_URL
- echo KUBE_CA_PEM_FILE=$KUBE_CA_PEM_FILE
- echo KUBE_TOKEN=$KUBE_TOKEN
- echo KUBE_NAMESPACE=$KUBE_NAMESPACE
- kubectl config set-cluster "$CI_PROJECT_ID" --server="$KUBE_URL" --certificate-authority="$KUBE_CA_PEM_FILE"
- kubectl config set-credentials "$CI_PROJECT_ID" --token="$KUBE_TOKEN"
- kubectl config set-context "$CI_PROJECT_ID" --cluster="$CI_PROJECT_ID" --user="$CI_PROJECT_ID" --namespace="$KUBE_NAMESPACE"
- kubectl config use-context "$CI_PROJECT_ID"
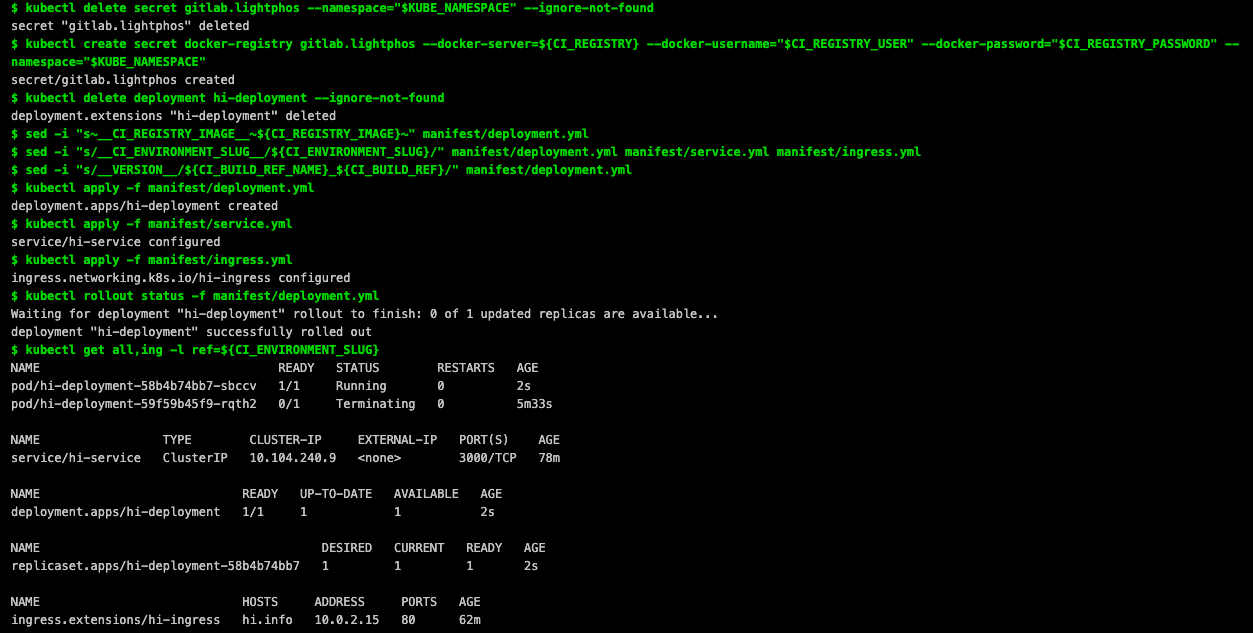
- kubectl delete secret gitlab.lightphos --namespace="$KUBE_NAMESPACE" --ignore-not-found
- kubectl create secret docker-registry gitlab.lightphos --docker-server=${CI_REGISTRY} --docker-username="$CI_REGISTRY_USER" --docker-password="$CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD" --namespace="$KUBE_NAMESPACE"
- kubectl delete deployment hi-deployment --ignore-not-found
- sed -i "s~__CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE__~${CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE}~" manifest/deployment.yml
- sed -i "s/__CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUG__/${CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUG}/" manifest/deployment.yml manifest/service.yml manifest/ingress.yml
- sed -i "s/__VERSION__/${CI_BUILD_REF_NAME}_${CI_BUILD_REF}/" manifest/deployment.yml
- kubectl apply -f manifest/deployment.yml
- kubectl apply -f manifest/service.yml
- kubectl apply -f manifest/ingress.yml
- kubectl rollout status -f manifest/deployment.yml
- kubectl get all,ing -l ref=${CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUG}
manifest/deployment.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hi-deployment
labels:
app: hi
ref: __CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUG__
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hi
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hi
ref: __CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUG__
spec:
containers:
- name: hi
image: __CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE__:__VERSION__
ports:
- containerPort: 8090
imagePullSecrets:
- name: gitlab.lightphos
manifest/service.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hi-service
labels:
app: hi
ref: __CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUG__
spec:
type: NodePort
externalIPs:
- 192.168.99.101
selector:
app: hi
ports:
- port: 3000
nodePort: 30002
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8090
Push and see the pipeline deployed on to k8s. NOTE: Select hi-3-production namespace. (3 is the project id in our local gitlabs)
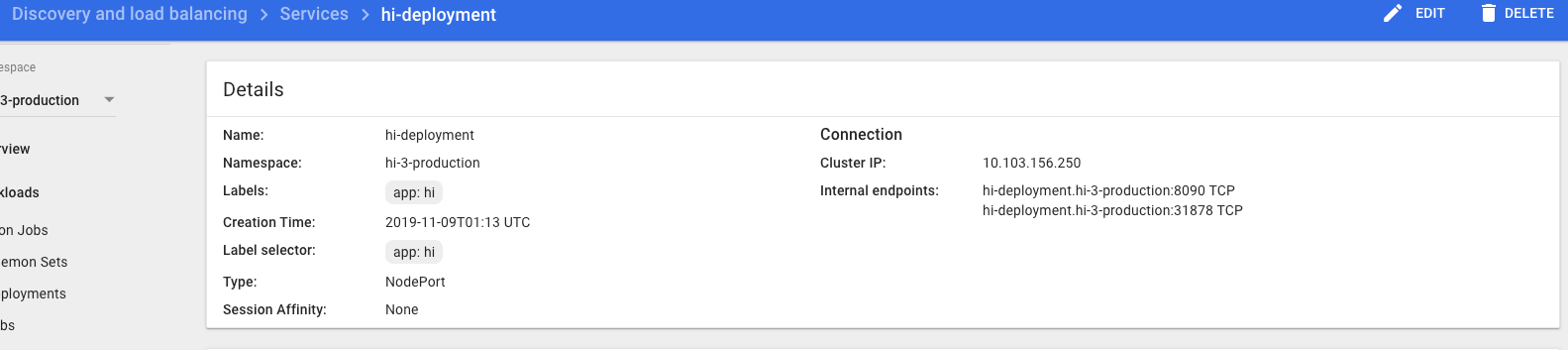
Image:
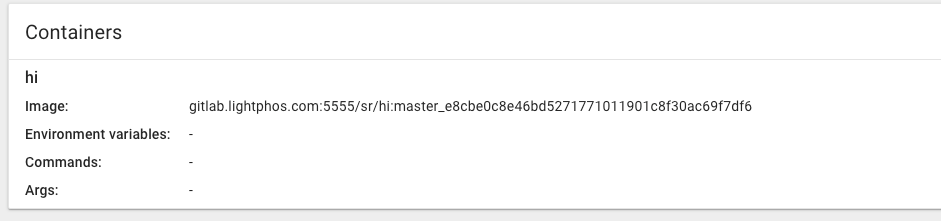
Service
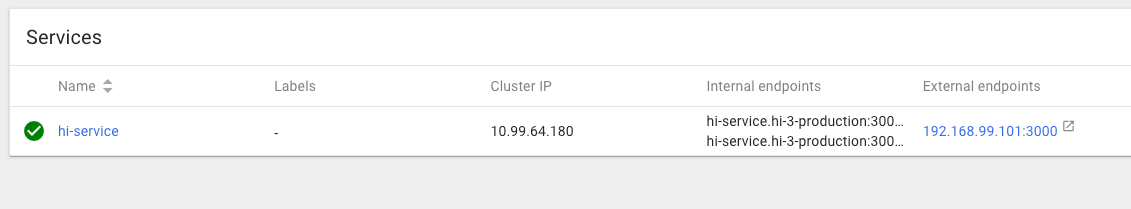
Check it out
minikube service hi-service --namespace=hi-3-production
or
Click on the service link button
Or
From Gitlab environments -> Production -> Open Live Environment Button
Should take you to
http://192.168.99.101:3000/earth
Ingress
Add an Nginx Ingress LB. Note with Ingress added service.yml does not need NodePort or external IP. We will access the site via a host name, hi.info.
minikube addons enable ingressCheck it's up
kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep nginx-ingress-controller
Logs:
kubectl logs -f -n kube-system $(kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep nginx-ingress-controller | cut -f 1 -d ' ')
Config:
kubectl exec -it -n kube-system <nginx ingress controller> cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
manifest/ingress.yml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1 # for versions before 1.14 use extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: hi-ingress
labels:
app: hi
ref: __CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUG__
# annotations:
# nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /$1 <- stops request parameters being passed
spec:
rules:
- host: hi.info
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: hi-service
servicePort: 3000
Apply it (add to .gitlabci.yml, the following)
kubectl apply -f manifest/ingress.yml
Add minikube ip and hostname hi.info to /etc/hosts
echo "$(minikube ip) hi.info" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Browse
Voila ...
Using a Fixed Namespace
Based on this excellent post: https://edenmal.moe/post/2019/GitLab-Kubernetes-Using-GitLab-CIs-Kubernetes-Cluster-feature/#gitlab-ci-kubernetes-cluster-feature
- Create the namespace on k8s
kubectl create ns lightphos - Apply the rbac.yml file (below)
kubectl apply -f manifest/rbac.yml - Get the encoded CA and Token
kubectl get -n lightphos secret $(kubectl get -n lightphos secret | grep gitlab-ci | cut -f 1 -d ' ') -o yaml - Decode from base64
echo <CA> | base64 --decode, echo <Token> | base64 --decode - Add it to gitlab -> operations -> kubernetes.
- Set the Project namespace to lightphos, untick Gitlab-managed cluster
- Deploy the project. Gitlab ci file .gitlab-ci.yml should not need to change.
- The code will now be deployed to lightphos namespace.
The site should be available as usual at http://hi.info
manifest/rbac.yml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: gitlab-ci
namespace: lightphos
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: lightphos
name: gitlab-ci
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
- apiGroups: ["extensions"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
- apiGroups: ["autoscaling"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
- apiGroups: ["networking.k8s.io"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: gitlab-ci
namespace: lightphos
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: gitlab-ci
namespace: lightphos
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: gitlab-ci
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Console output of deploy stage of gitlab ci pipeline: